Configure ZTNA for hosted resources with Azure container instances
In this topic, you will learn how to configure Portnox™ Zero Trust Network Access to allow your users to access your private web applications hosted in Microsoft Azure and accessible within an Azure private network, by using a Docker container in an Azure container instance.
In this scenario:
-
You want your on-premises and remote users to be able to access private web applications that are hosted in Azure.
-
You need to host a Portnox Docker container in Azure, for example, in Azure container instances, and in the same Azure virtual network as the hosted web applications.
We assume that you have already configured Azure, a virtual network in Azure, and that another container instance runs a web application, accessible via HTTP within your Azure local network. We also assume that you already distributed certificates to your client devices.
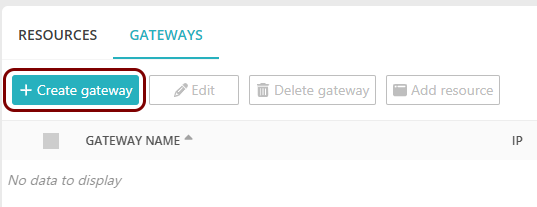
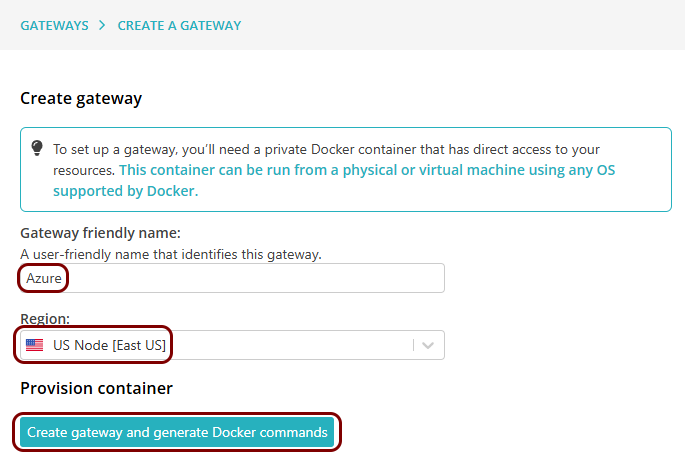
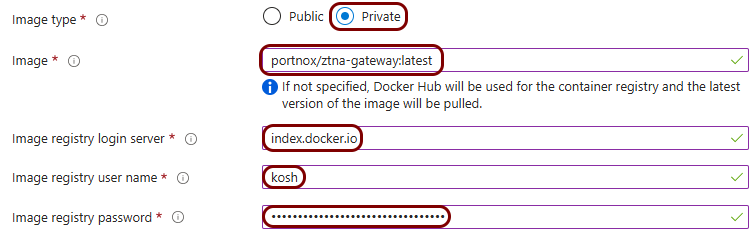
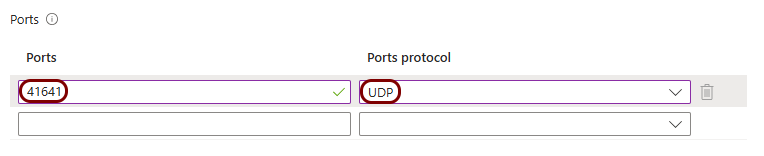
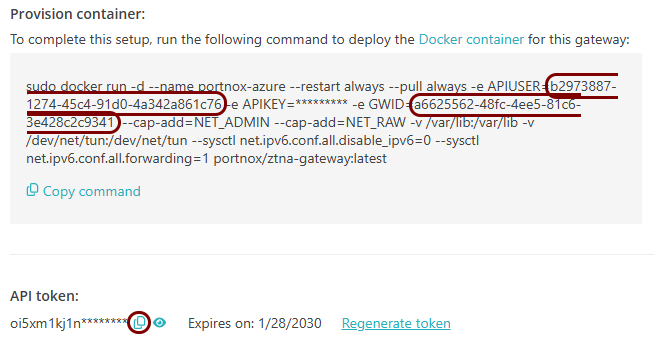
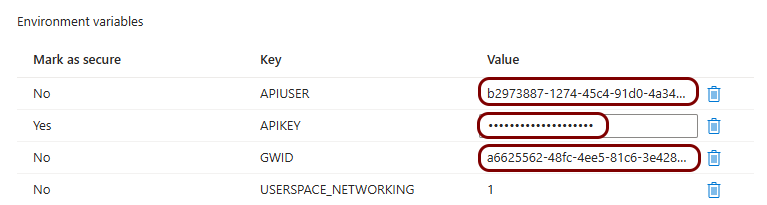
Set up the ZTNA gateway in Portnox Cloud
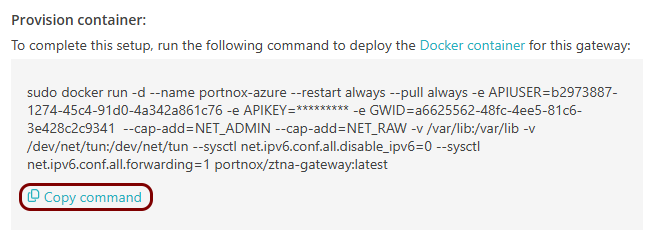
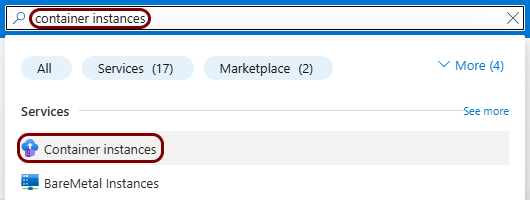
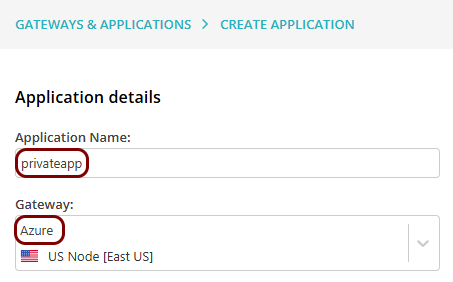
In this section, you will set up a ZTNA gateway in Portnox Cloud, create a container instance in Azure, and run the Portnox ZTNA Docker container.
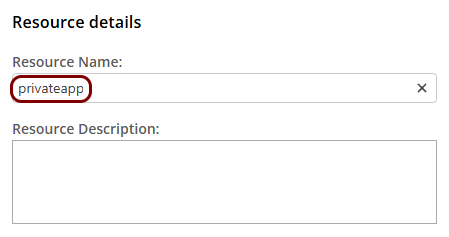
Set up the ZTNA resource in Portnox Cloud
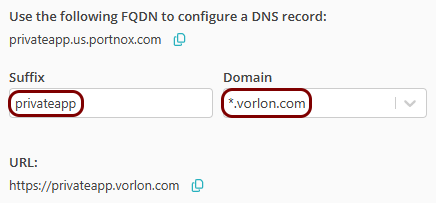
In this section, you will set up a ZTNA resource in Portnox Cloud and configure it to access your private web application hosted in the same virtual network as the Docker container.
Result: Your users can now access your private resource by typing the URL in the browser.
Configure the hosted application access control policy
In this section, you will configure the access control policy for groups that you want to have access to this hosted application.