Deploy the local RADIUS server container using Docker Desktop on Windows
In this topic, you will learn how to deploy the Portnox™ Cloud local RADIUS server container using Docker Desktop on a local Windows machine (physical or virtual).
Read the following important information before you begin:
-
We assume that the Windows machine is already installed, configured, updated, and connected to the local network. This guide includes only the installation and configuration of Docker Desktop and the Portnox Cloud local RADIUS server container.
-
You cannot place NAS devices behind a NAT because the local RADIUS server uses the source IP address of the connection, and with a NAT in place, that address would be the same for several NAS devices.
-
We recommend running Portnox Docker containers using Linux for performance reasons. Portnox Docker images are built for Linux so in Windows, they have to be run using virtualization. If you run Docker Windows in a virtual machine, you will need nested virtualization, which can affect performance.
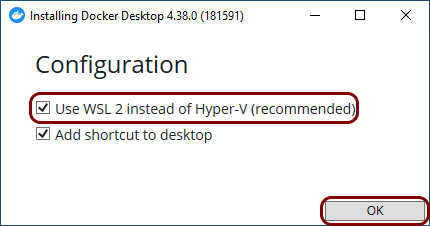
Install Docker Desktop
In this section, you will learn how to follow Docker documentation to install Docker Desktop on the Windows machine.
Skip this section if Docker Desktop is already installed.
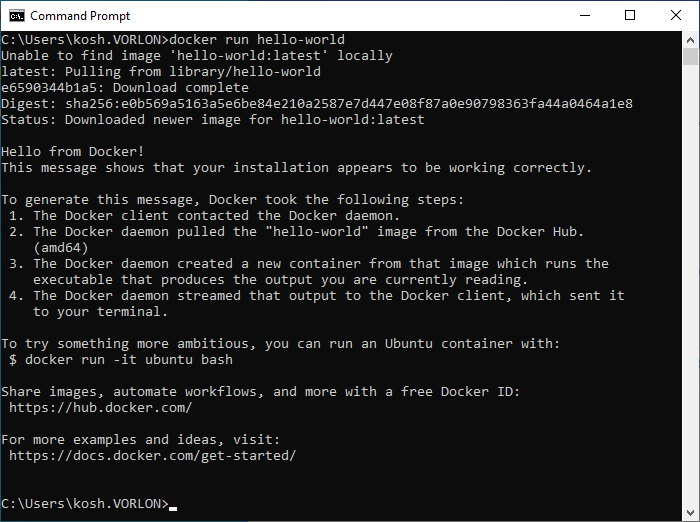
Run the Portnox Cloud local RADIUS container
In this section, you will deploy the local RADIUS server Docker container locally to the Windows machine.
Result: Your local RADIUS server is active.
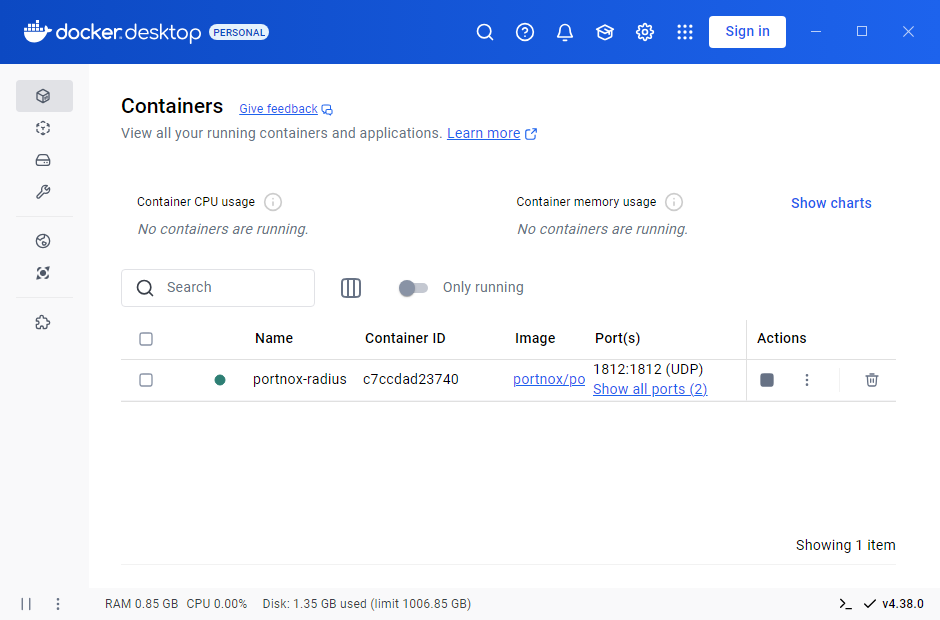
You can check its status in Portnox Cloud, in the section.

Automatically update the existing local container
In this section, you will learn how to automatically update your Docker container to the latest version by deploying another Docker container: portnox-autoupdate.
Remove an existing local RADIUS container
In this section, you will learn how to manually remove an existing local RADIUS container.