Deploy the local TACACS+ server container in Amazon Web Services (AWS)
In this topic, you will learn how to deploy the Portnox™ Cloud local TACACS+ server container in Amazon Web Services (AWS) using AWS Fargate.
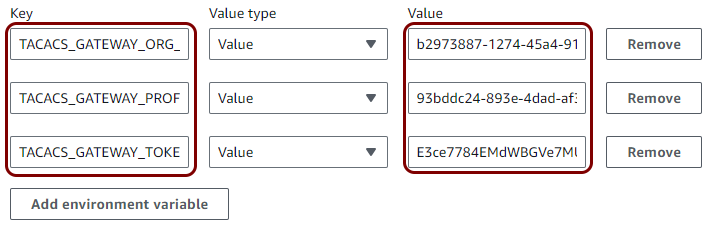
To deploy the local TACACS+ server Docker container in AWS Container Instances, you must first configure the settings for the local TACACS+ server container and generate environment variables. To do it, go to the following topic: Run the local TACACS+ server in a container.
Read the following important information before you begin:
-
AWS Fargate is one of the options to deploy the local TACACS+ server container in AWS. Other options include using Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) or EC2 instances. If you choose a different option, please follow the relevant AWS documentation for your chosen method.
-
In order for the local TACACS+ server container in AWS to be able to communicate with your NAS devices in your local network, you must create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in AWS and connect it to your local network. AWS offers many ways of achieving this. This topic is beyond the scope of this guide, but you can find useful information in the following AWS documentation topic: Connect your VPC to remote networks using AWS Virtual Private Network.
-
You cannot place NAS devices behind a NAT because the local TACACS+ server uses the source IP address of the connection, and with a NAT in place, that address would be the same for several NAS devices.
-
When you’re using stateless containers and you want to update to a newer version of the Docker image, you need to delete the container and recreate it from scratch with the same parameters.
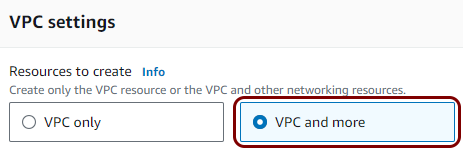
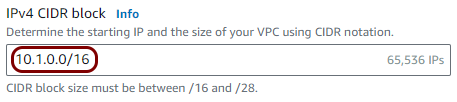
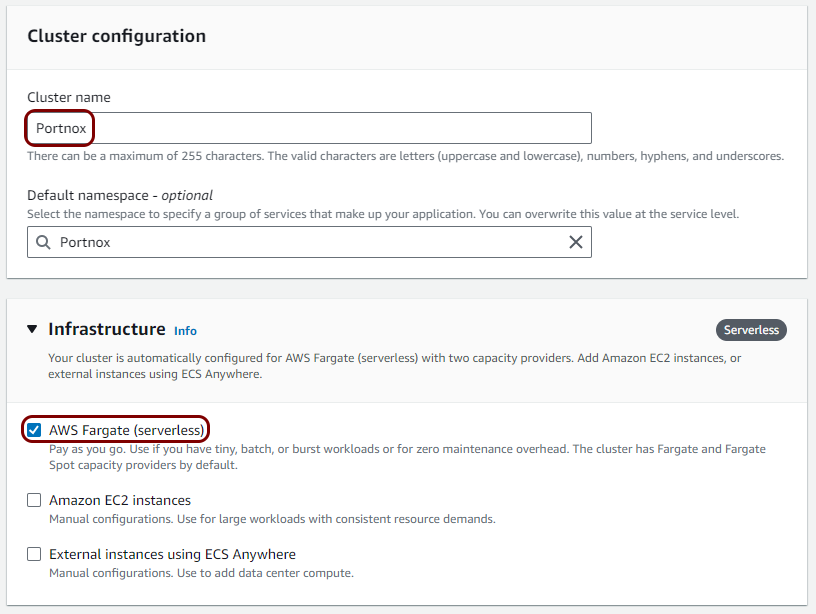
Create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
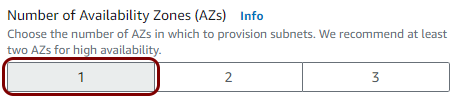
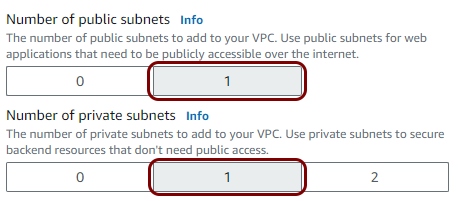
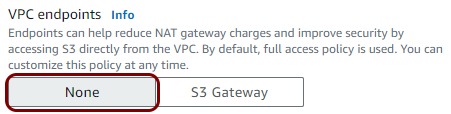
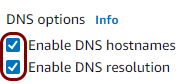
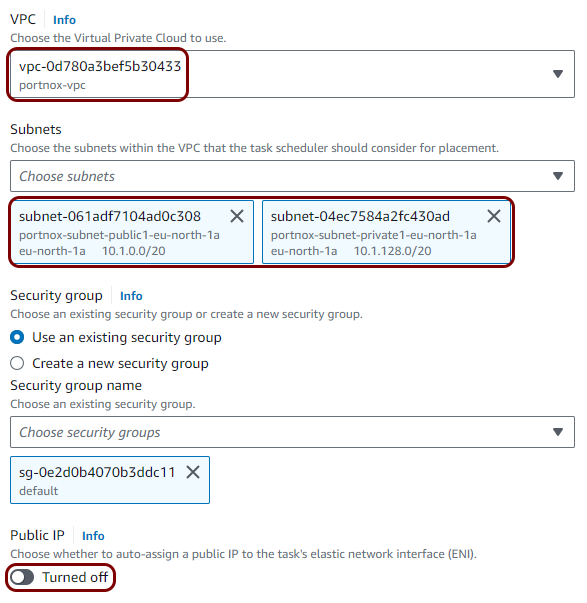
In this section, you will create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with a private subnet for local TACACS+ server containers.
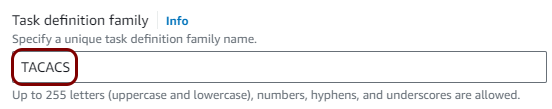
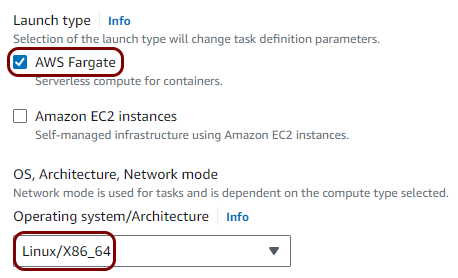
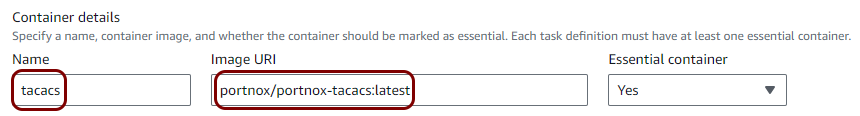
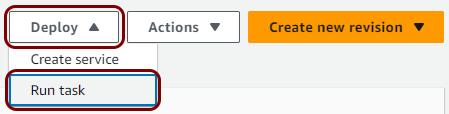
Create a task definition and a cluster
In this section, you will deploy the local TACACS+ server Docker container to the Virtual Private Cloud created in the previous step by creating a task definition and a cluster.
Result: Your local TACACS+ server is active.

You can check its status in Portnox Cloud, in the section.
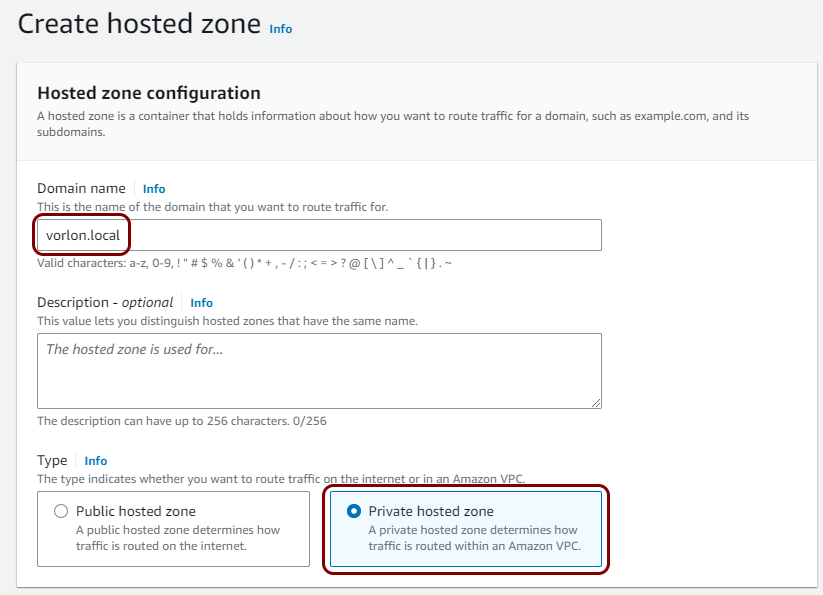
Create a private hosted DNS zone
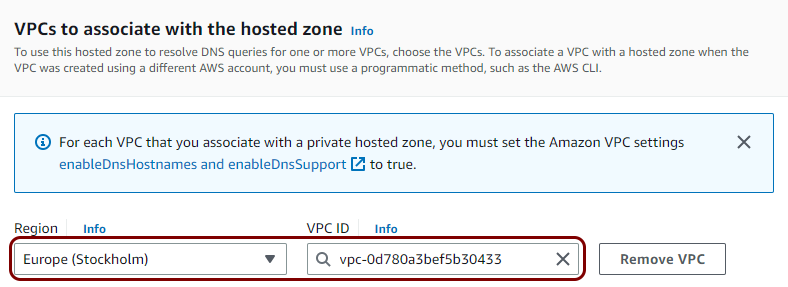
In this section, you will create a private hosted DNS zone for your Virtual Private Cloud, which lets you configure your NAS devices to access the local TACACS+ server using a fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) instead of its IP address.
Every time that you stop and restart your local TACACS+ server container in AWS, it may be assigned a different IP address on the subnet, which means you would have to reconfigure your NAS devices after every restart. Unfortunately, at this time, AWS does not offer any method to maintain a fixed IP address on its virtual private cloud.
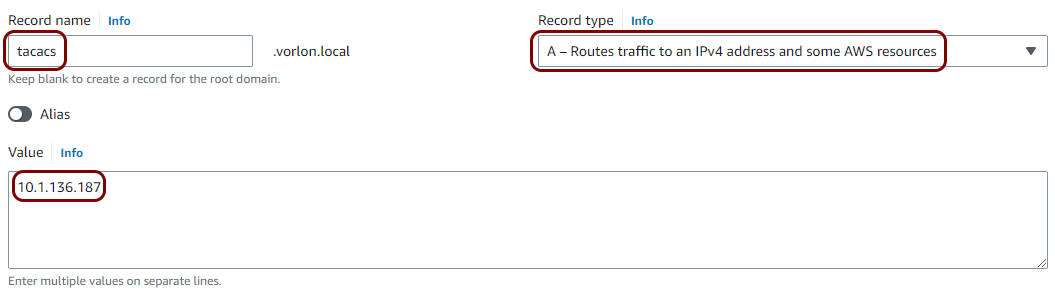
To overcome this problem, you can configure a private hosted DNS zone in AWS, assign a private FQDN to the local TACACS+ server, and configure the NAS devices to access this server using this FQDN. This way, if you need to restart the container and get a different IP address, you can just change the IP address in the zone definition instead of having to reconfigure every NAS device.
Result: You can configure your NAS devices in the VPC to access the local TACACS+ server using its FQDN (in our example, tacacs.vorlon.local) in the VPC instead of its IP address (in our example, 10.1.136.187). You also need to configure the resolver in the NAS device to use one of the AWS DNS servers listed in the NS record, in the Value field.

If you need to restart the container and the IP address of the local TACACS+ server changes, change the IP address in the record that you created for your hosted zone.