Integrate with Datadog using a syslog forwarder and TLS
In this topic, you will learn how to send Portnox™ Cloud alerts to the Datadog SIEM solution using a syslog forwarder with TLS for increased security.
To integrate with Datadog using a syslog forwarder and TLS:
- Deploy a machine or a virtual machine as a syslog message collector.
- Install syslog-ng (or similar software) on this machine and accept syslog events via TLS from Portnox Cloud.
- Send the syslog events to the Datadog HTTPS intake API via HTTPS.
In this example configuration, we are using a virtual machine in Microsoft Azure with syslog-ng and a TLS connection. Using this configuration, the entire communications is encrypted using TLS (Portnox Cloud to syslog collector) and HTTPS (syslog collector to Datadog).
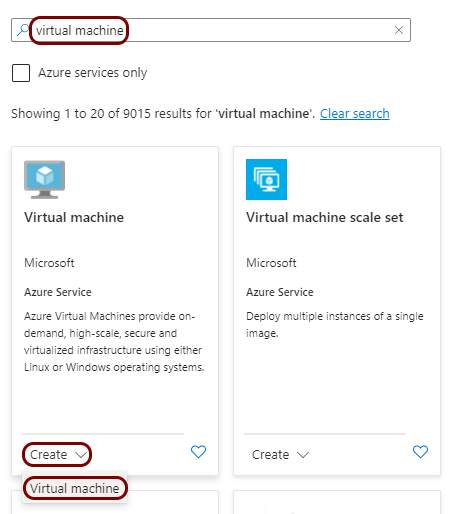
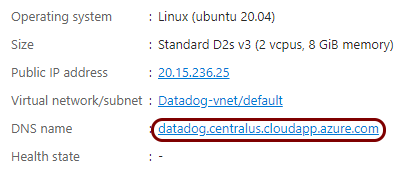
Create a Linux virtual machine
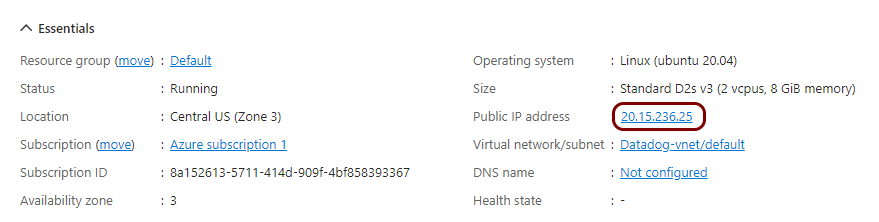
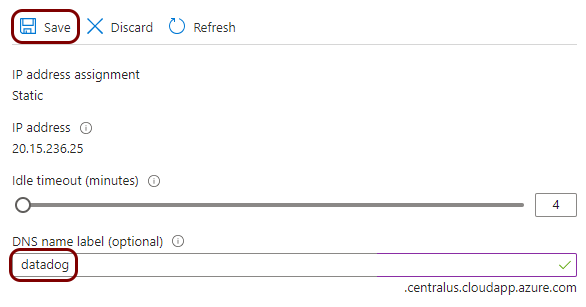
To integrate with Datadog, you need to run syslog software on a physical or virtual machine, so that it can collect alert data from Portnox™ Cloud and send that data to Datadog. In this section, you will learn how to create and configure such a virtual machine in Microsoft Azure based on the Linux Ubuntu operating system.
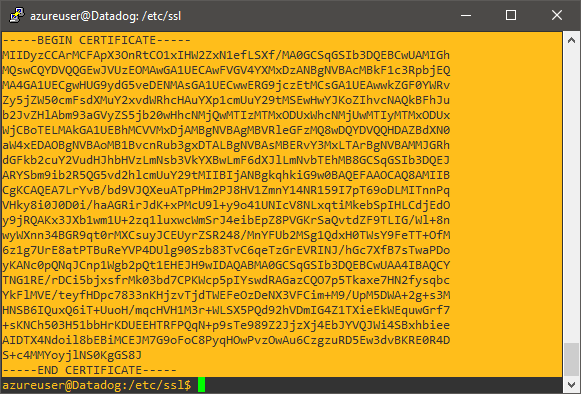
Generate a certificate for your syslog collector
In this section, you will use OpenSSL software on the virtual machine to generate a self-signed certificate, which Portnox Cloud will use to connect to the collector via TLS.
Install and configure syslog-ng
In this section, you will install syslog-ng on the virtual machine, and configure it to accept events from the network via TLS and send them to Datadog via HTTPS.
- In your SSH window, type the following commands: sudo apt-get update and sudo apt-get install syslog-ng to install syslog-ng software.
- Then, type the following command: sudo nano /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf to edit syslog-ng configuration.
-
Follow the steps described in the Datadog documentation for syslog-ng to add the following configuration sections to the
syslog-ng.conf file but modify them as follows:
- In your SSH window, type the following command: sudo systemctl restart syslog-ng to restart syslog-ng after configuration changes.
Result: The syslog-ng software is configured, running, and waiting for events coming through TLS from Portnox Cloud.
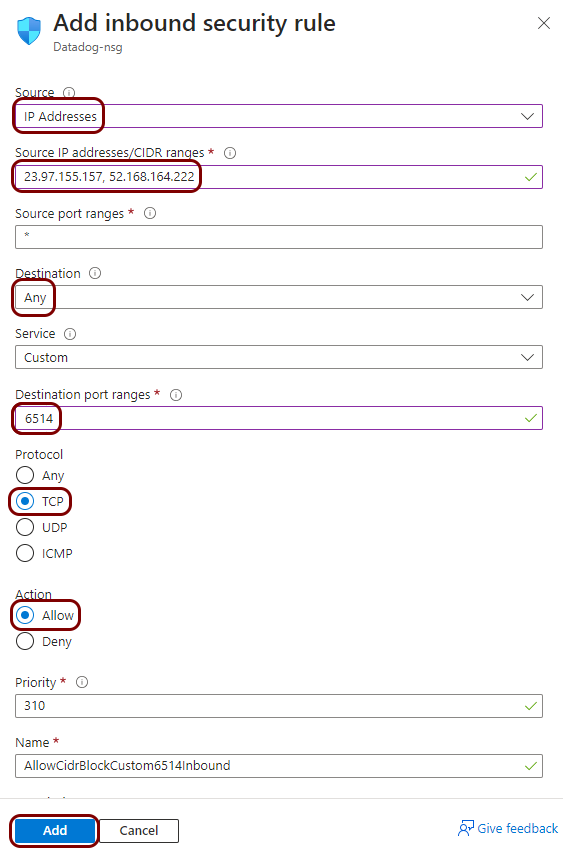
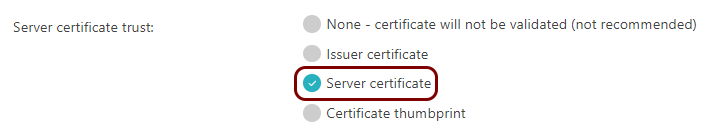
Configure Portnox Cloud
In this section, you will learn how to configure Portnox™ Cloud to send alert data using TLS to the virtual machine with syslog-ng so that it forwards the data to the Datadog intake.
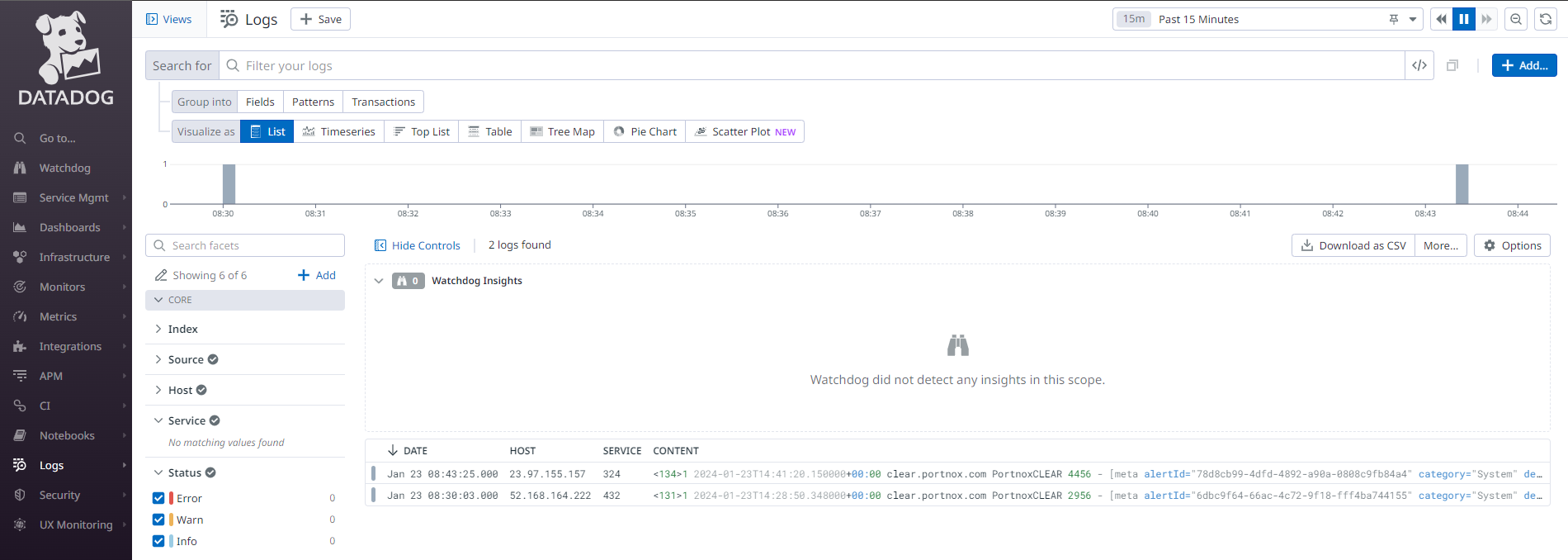
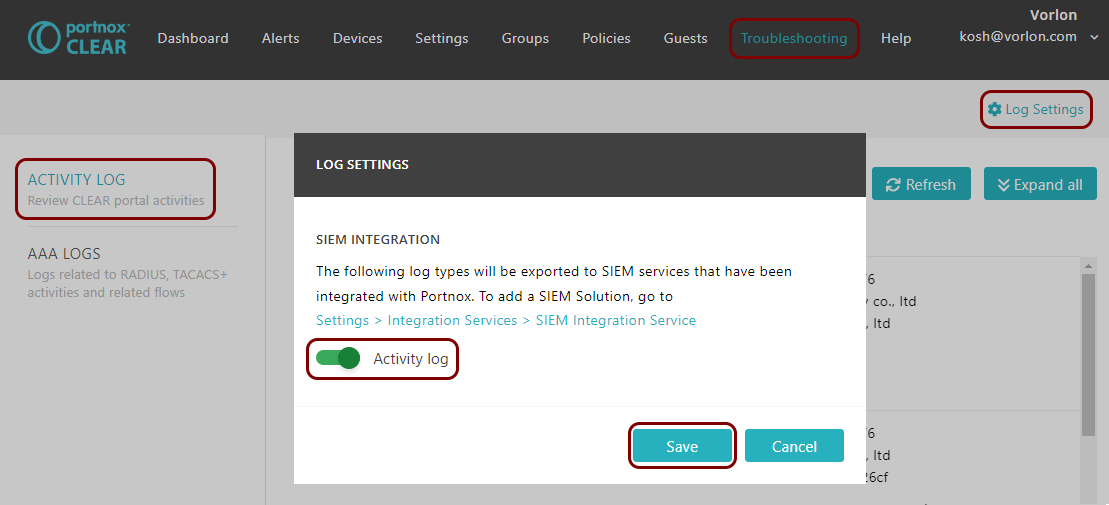
Result: Datadog is receiving alerts from Portnox Cloud through a secure connection.
You can confirm that, for example, by accessing the Log Explorer.