Onboard an iPhone to a Wi-Fi network with credentials and a custom profile
In this topic, you will learn how to onboard using credentials, an iPhone with iOS, a Wi-Fi network managed by Portnox™ Cloud, and a custom profile created with the iMazing Profile Editor.
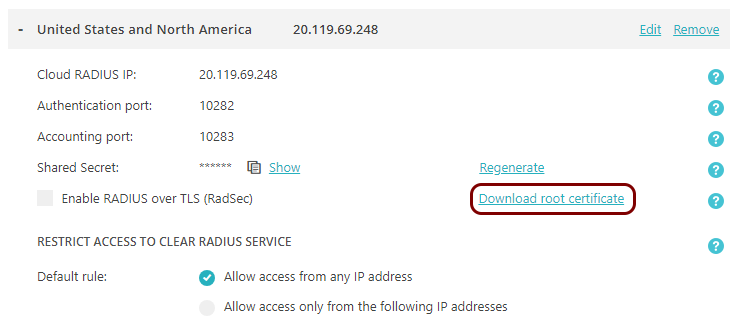
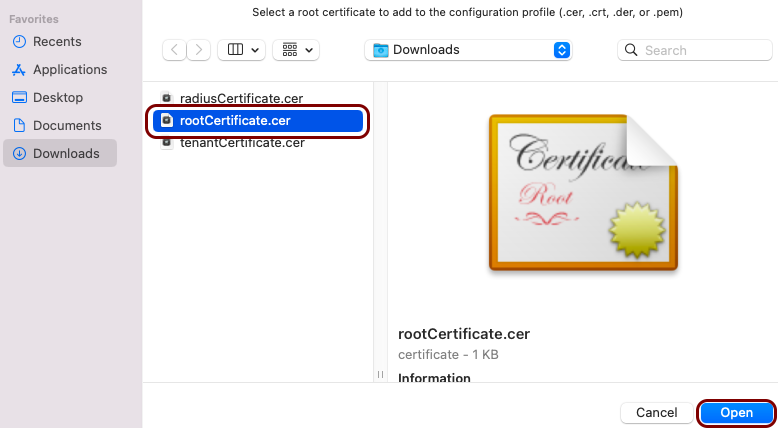
Download the root CA certificate
In this section, you will download the root CA certificate from Portnox™ Cloud, which is needed to create a profile.
Result: The root CA certificate file is in the Downloads folder on the local disk.
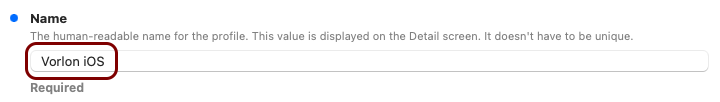
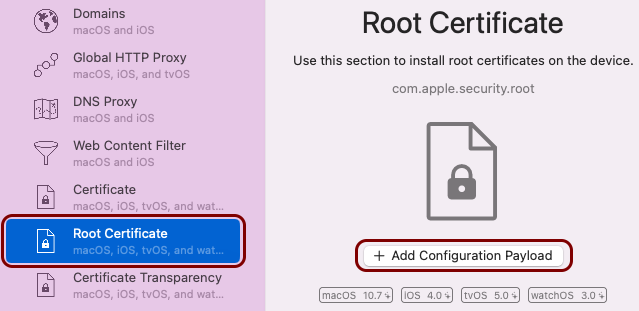
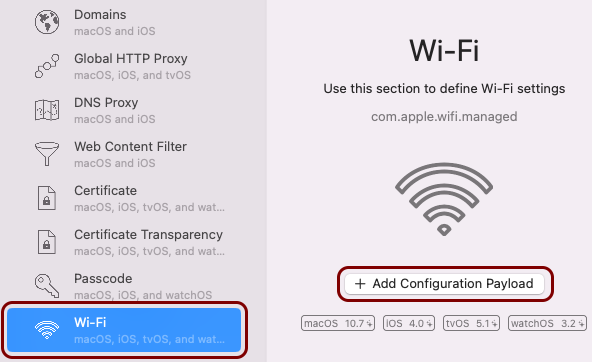
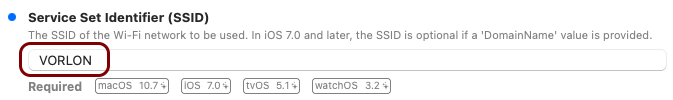
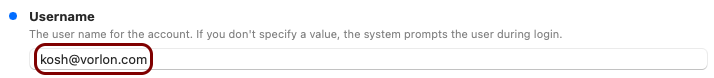
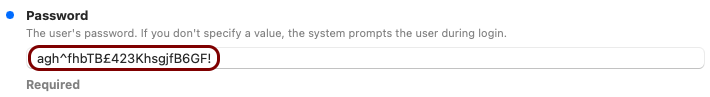
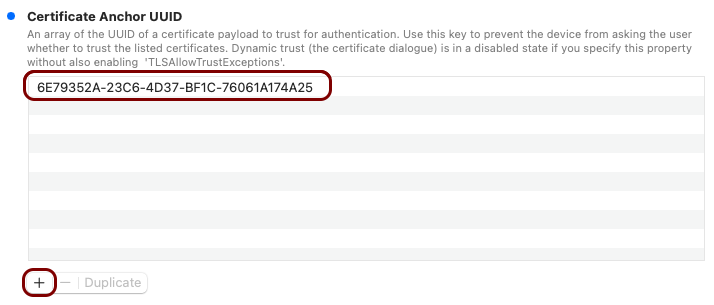
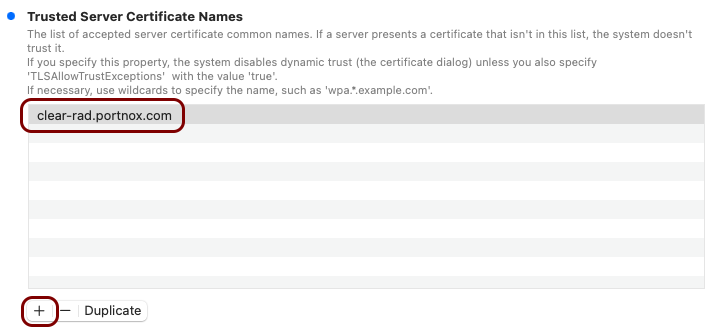
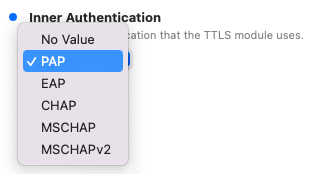
Create the custom profile
In this section, you will use the iMazing Profile Editor to create an Apple profile for use with your iOS devices, which contains the following payloads: the root CA certificate and the Wi-Fi configuration.
Result: The custom profile file (.mobileconfig) is saved on the disk and ready to be copied to your iOS device.
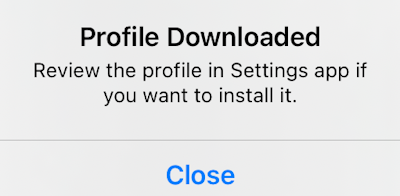
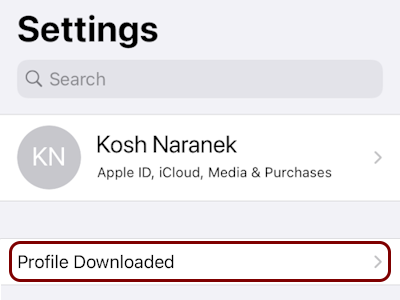
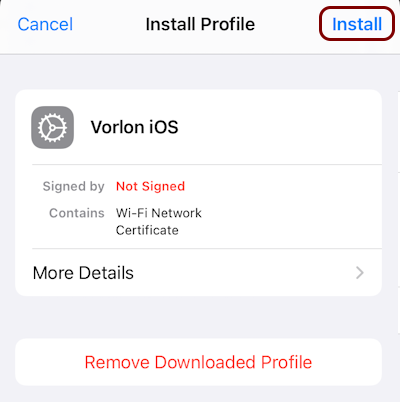
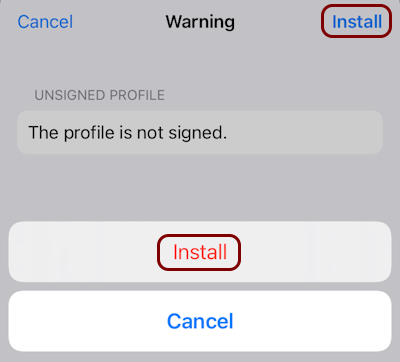
Install the custom profile
In this section, you will learn how to install the custom profile on your iOS device.
Before you can install your custom profile, you need to copy it to your iOS device. For example, you can send the profile file using email, instant messaging, upload it to cloud storage, or transfer it using Bluetooth..
Result: You downloaded and installed the profile and can now connect to the enterprise network.
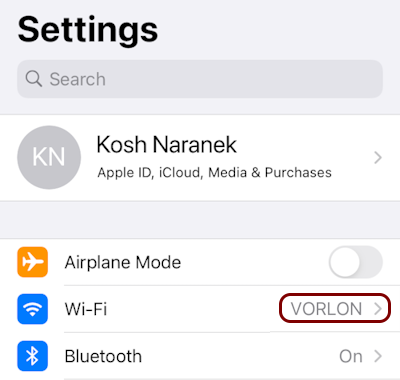
Troubleshooting information: See the following topic: How to troubleshoot typical device onboarding issues.